Key Generation Algorithm Digital Signature
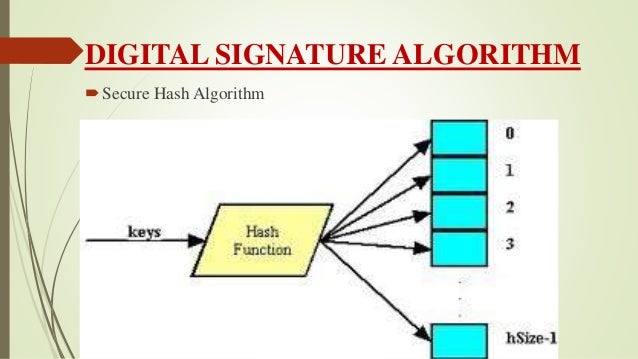
The RSA signature generation process and the encoding of the result is described in detail in PKCS #1. 2.2.2 DSA Signature Algorithm The Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) is defined in the Digital Signature Standard (DSS). DSA was developed by the U.S. Government, and DSA is used in conjunction with the SHA-1 one-way hash function. A digital signature algorithm allows an entity to authenticate the integrity of signed data and the identity of the signatory. The recipient of a signed message can use a digital signature as evidence in demonstrating to a third party that the signature was, in fact, generated by the claimed signatory. Dec 01, 2016 This video describes the key generation for the DSA. An example with artificially small numbers is also given. Applied Cryptography: The Digital Signature Algorithm - Part 1 Leandro Junes. Jun 06, 2016 What is digital signature? - Duration: 5:03. Public Key Cryptography - Computerphile - Duration: 6:20. Public Key Cryptography: RSA Encryption Algorithm - Duration: 16:31.
-->Digital Signature Standard Algorithm
Cryptographic digital signatures use public key algorithms to provide data integrity. When you sign data with a digital signature, someone else can verify the signature, and can prove that the data originated from you and was not altered after you signed it. For more information about digital signatures, see Cryptographic Services. Windows vista ultimate key generator free download.
This topic explains how to generate and verify digital signatures using classes in the System.Security.Cryptography namespace.
Generating Signatures
Digital signatures are usually applied to hash values that represent larger data. The following example applies a digital signature to a hash value. First, a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class is created to generate a public/private key pair. Next, the RSACryptoServiceProvider is passed to a new instance of the RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter class. This transfers the private key to the RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter, which actually performs the digital signing. Before you can sign the hash code, you must specify a hash algorithm to use. This example uses the SHA1 algorithm. Finally, the CreateSignature method is called to perform the signing.
Due to collision problems with SHA1, Microsoft recommends SHA256 or better.
Signing XML Files
The .NET Framework provides the System.Security.Cryptography.Xml namespace, which enables you sign XML. Signing XML is important when you want to verify that the XML originates from a certain source. For example, if you are using a stock quote service that uses XML, you can verify the source of the XML if it is signed.
The classes in this namespace follow the XML-Signature Syntax and Processing recommendation from the World Wide Web Consortium.
Verifying Signatures
To verify that data was signed by a particular party, you must have the following information:
Digital Signature Algorithm Example
The public key of the party that signed the data.
The digital signature.
The data that was signed.
The hash algorithm used by the signer.
To verify a signature signed by the RSAPKCS1SignatureFormatter class, use the RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter class. The RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter class must be supplied the public key of the signer. You will need the values of the modulus and the exponent to specify the public key. (The party that generated the public/private key pair should provide these values.) First create an RSACryptoServiceProvider object to hold the public key that will verify the signature, and then initialize an RSAParameters structure to the modulus and exponent values that specify the public key.
The following code shows the creation of an RSAParameters structure. The Modulus property is set to the value of a byte array called modulusData and the Exponent property is set to the value of a byte array called exponentData.
After you have created the RSAParameters object, you can initialize a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class to the values specified in RSAParameters. The RSACryptoServiceProvider is, in turn, passed to the constructor of an RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter to transfer the key.
The following example illustrates this process. In this example, hashValue and signedHashValue are arrays of bytes provided by a remote party. The remote party has signed the hashValue using the SHA1 algorithm, producing the digital signature signedHashValue. The RSAPKCS1SignatureDeformatter.VerifySignature method verifies that the digital signature is valid and was used to sign the hashValue.
Key Generation Algorithm Digital Signature Card
Windows 7 64 bit cd key generator. This code fragment will display 'The signature is valid' if the signature is valid and 'The signature is not valid' if it is not.